Animation
Animation is a powerful medium that brings pictures, characters, and stories to life, enthralling audiences across the world. Whether you’re new to animation or want to improve your skills, knowing its concepts and tools can help you succeed in this fascinating field. This tutorial delves further into animation, focusing on high-search-volume keywords and designed for both beginners and pros.
What is Animation?
Animation refers to the process of creating the illusion of movement by displaying a sequence of images, drawings, or models. This technique can be achieved using various tools and technologies, including traditional methods and digital software.
Key benefits of animation:
- Engagement: Animations grab attention and convey messages effectively.
- Versatility: Used in movies, advertisements, educational tools, and gaming.
- Creativity: Encourages storytelling and imaginative designs.
Types of Animation
Understanding the different types of animation is crucial to choosing the right approach for your project.
1. Traditional Animation
Traditional animation, often known as cel animation, is a time-honored approach in visual storytelling that includes hand sketching each frame. This art style, developed in the early twentieth century, has been a pillar of the animation industry and is still acclaimed for its rich visual appeal and exquisite workmanship.

Also known as 2D animation, this method involves drawing each frame by hand. Disney’s early works are classic examples.
- Tools: Pencil, paper, light tables.
- Popular for: Storytelling, explainer videos.
2. 3D Animation
3D animation is a dynamic and adaptable creative technique that creates three-dimensional moving pictures in a digital environment. Unlike conventional animation, which is based on hand-drawn frames, 3D animation employs computer software to model, rig, and animate objects and people, giving them depth and realism. This contemporary approach has transformed the world of narrative and entertainment, with prominent roles in films, video games, and virtual reality experiences.
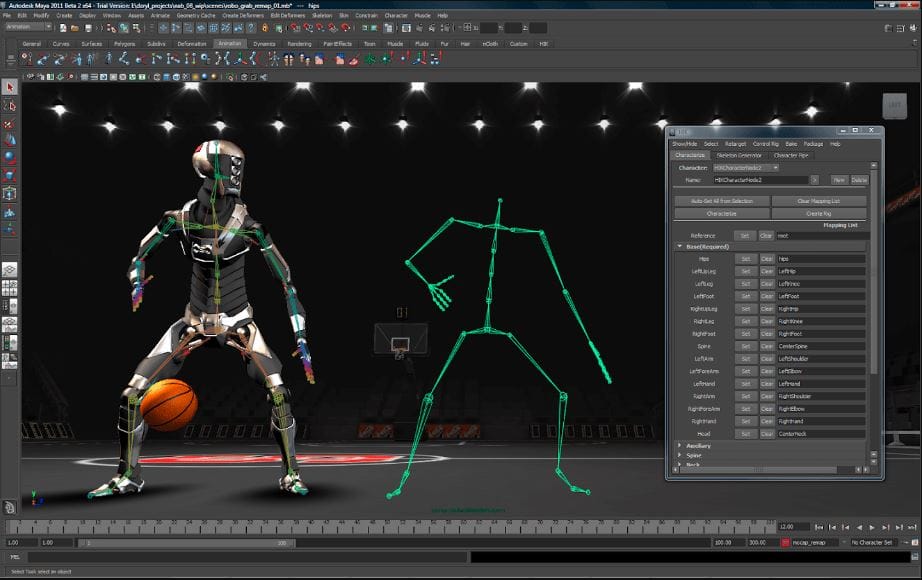
3D animation creates lifelike characters and environments using computer software. It’s widely used in movies, video games, and simulations.
- Tools: Blender, Maya, 3ds Max.
- Popular for: Action-packed movies, architectural visualization.
3. Motion Graphics
Motion graphics is a computer animation approach that uses graphic design concepts with animation to generate dynamic and captivating images. It prioritizes animating text, forms, symbols, and other graphical components above fully developed characters and complex 3D settings. This adaptable medium is frequently employed in advertising, movies, social media, and site design, providing an effective means of communicating ideas and information.
Motion graphics focus on animating text, shapes, and designs rather than characters. It’s often used for branding, advertising, and explainer videos.

- Tools: Adobe After Effects, Cinema 4D.
- Popular for: Corporate videos, educational content.
4. Stop Motion
Stop motion animation is a unique and compelling filmmaking method that involves manipulating and photographing actual things frame by frame to create the appearance of movement. Unlike conventional or computer-generated animation, stop motion uses actual materials like clay, puppets, paper, and even common items. When a sequence of photos is played back at fast speed, it creates a smooth motion illusion.
Stop motion involves photographing physical objects in small increments to simulate movement. Think of classics like Wallace and Gromit.

- Tools: Cameras, clay models, puppets.
- Popular for: Artistic and quirky projects.
5. Whiteboard Animation
Whiteboard animation is a kind of video production that use hand-drawn animation techniques to visually tell a tale, explain a concept, or demonstrate an idea. It usually shows a simulated hand sketching or writing on a white backdrop, complemented by voiceover narration and music. This engaging and simplistic animation style is popular for educational content, marketing, and explainer videos due to its clarity and ability to hold the viewer’s attention.
Whiteboard animation mimics the experience of drawing on a whiteboard. It’s popular for educational content and explainer videos.

- Tools: Doodly, Videoscribe.
- Popular for: Tutorials, business presentations.
Core Principles of Animation
Mastering animation requires understanding its fundamental principles, originally outlined by Disney animators in The Illusion of Life:
- Squash and Stretch: Adds elasticity to movements, making characters more lifelike.
- Anticipation: Prepares the viewer for an action, adding realism.
- Staging: Ensures clarity in the narrative and directs the viewer’s attention.
- Timing and Spacing: Dictates the speed and fluidity of movement.
- Exaggeration: Enhances storytelling by amplifying emotions and actions.
“2D vs 3D animation”
| Aspect | 2D Animation | 3D Animation |
| Definition | Two-dimensional animation using height and width. | Three-dimensional animation with height, width, and depth. |
| Appearance | Flat and stylized, resembling hand-drawn or cartoon visuals. | Realistic or semi-realistic, with depth and perspective. |
| Creation Process | Drawn frame-by-frame; involves sketching, inking, and coloring. | Built using 3D modeling, rigging, and rendering. |
| Software | Adobe Animate, Toon Boom, TVPaint. | Maya, Blender, Cinema 4D, 3ds Max. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable due to simpler tools and techniques. | Higher due to advanced software and technical expertise. |
| Time Requirement | Time-intensive for frame-by-frame work. | Faster adjustments after initial asset creation. |
| Movement | Abstract and exaggerated. | Realistic and fluid, mimicking natural physics. |
| Learning Curve | Easier to learn for beginners. | More complex, requiring technical knowledge. |
| Reusability | Limited; frames and assets often need redrawing. | High; models and animations can be reused or adjusted easily. |
| Visual Style | Artistic and stylized; focuses on creativity over realism. | Detailed and dynamic; capable of creating lifelike visuals. |
| Applications | TV shows, web videos, educational content, and 2D games. | Feature films, video games, virtual reality, and simulations. |
| Examples | The Lion King (1994), SpongeBob SquarePants. | Toy Story, Frozen, Avatar. |
How to Create Animation
Follow these steps to bring your animation project to life:
1. Ideation
- Outline your concept and script.
- Sketch character designs and storyboards.
2. Tool Selection
Choose the right animation software for your project:
- Free Tools: Pencil2D, Synfig Studio, Blender.
- Paid Tools: Toon Boom Harmony, Autodesk Maya, Adobe Animate.
3. Design and Modeling
- Create characters, backgrounds, and props.
- Use layers to organize elements effectively.
4. Animation
- Animate keyframes for critical movements.
- Use in-between frames for smooth transitions.
5. Rendering
Convert your animation into a polished video format.
6. Post-Production
Add sound effects, voiceovers, and music for an immersive experience.
Top Animation Tools
1. Blender
- Features: 3D modeling, sculpting, and animation.
- Ideal for: Beginners and professionals.
2. Adobe Animate
- Features: 2D animation and interactive content creation.
- Ideal for: Web designers and animators.
3. Toon Boom Harmony
- Features: Advanced 2D animation and rigging.
- Ideal for: Studios and seasoned animators.
Best animation tools Download here!

Read More:- Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR), (XR) (2024) How it works ?

Hi, I’m Narinder Kumar, founder of BlogsBuz.com. I create articles and generate celebrity biographies, providing verified, up-to-date content. As an SEO expert and online tools creator, I also share practical tips on making money online, finance management, blogging, and passive income. My mission is to provide accurate information and keep you away from fake content, ensuring you stay well-informed and make smart decisions online.

Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
🌟 Thank you so much for visiting BlogsBuz.com! We’re thrilled to have you here 🙌
Stay tuned for daily updates on your favorite celebrities, trending news, and exclusive stories you won’t find anywhere else 🔥
👉 If you found this post helpful, please share it with your friends and spread the word!
Together, let’s make BlogsBuz.com your go-to source for all things entertainment 💫