4. Healthcare: Using Augmented Reality, surgeons may more accurately guide their surgeries by seeing the anatomy.
3. Virtual Meetings: Teams may work together in a shared virtual area using solutions like Meta’s Horizon Workrooms, which improves remote work by providing more engaging meetings.
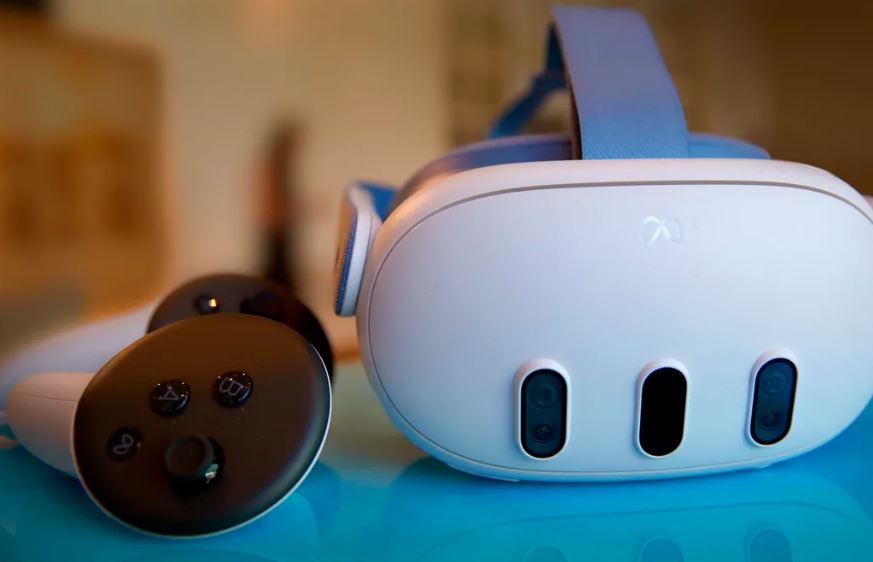
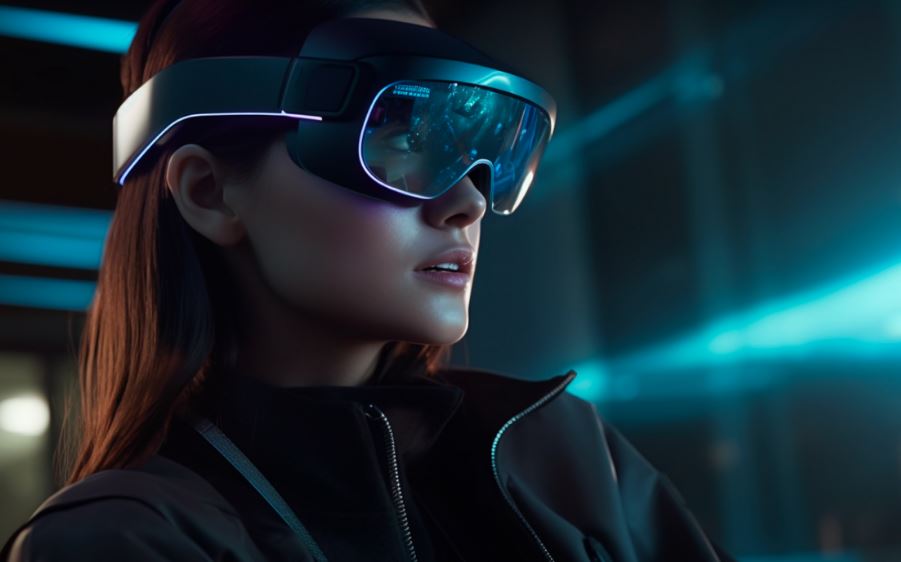
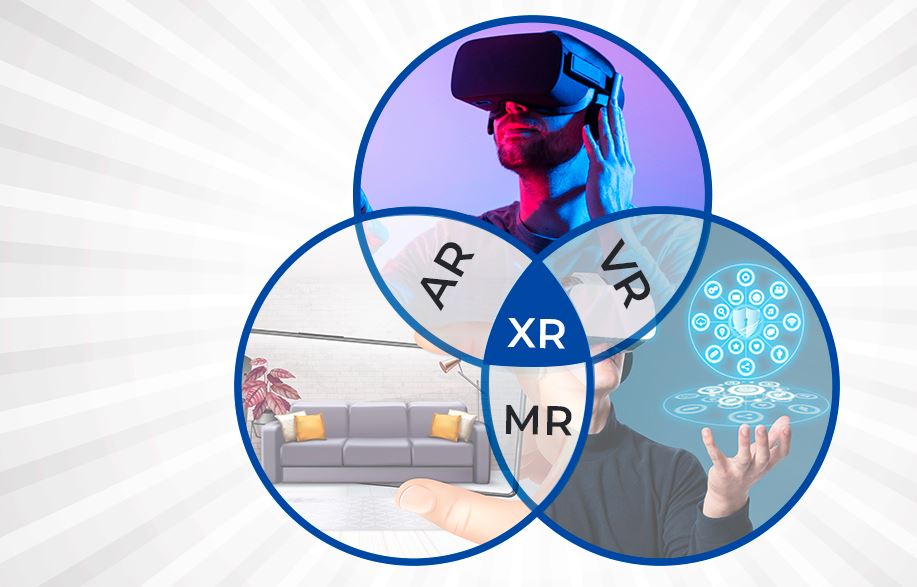
All immersive technologies, including augmented reality (Augmented Reality), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR), are together referred to as extended reality (XR). It encompasses the whole range of virtual and real-world settings made possible by wearables and computer technologies.
Any technology that combines the virtual and real worlds and enables users to engage with them or experience them to varying degrees is referred to as XR. (Augmented Reality), VR, MR, and any other immersive worlds that may emerge in the future are all included.
XR uses a mix of software (to generate 3D scenes, objects, and interactive features), sensors (to detect motions and surroundings), and hardware (such headsets, smartphones, and AR glasses). The real and virtual worlds collide with XR, enabling varying degrees of immersion.
[{"id":25769,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/free-ai-tools-for-editing-videos\/","name":"free-ai-tools-for-editing-videos","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/12\/top-5-video-editing-tool.jpg","alt":"top 5 video editing tool"},"title":"Top Free AI Tools for Editing Videos, Download, Tips & more.","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Dec 14, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-12-14 06:43:16","modifiedDate":"2024-12-14 06:43:19","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-12-14 06:43:19","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/ai\/' rel='post_tag'>AI<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/artificial-intelligence\/' rel='post_tag'>Artificial Intelligence<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/best-video-editor-tools-download\/' rel='post_tag'>best video editor tools download<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/free-ai-video-editor\/' rel='post_tag'>free AI video editor<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/top-5-video-editing-tool\/' rel='post_tag'>top 5 video editing tool<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/top-free-ai-tools-for-editing-videos\/' rel='post_tag'>Top Free AI Tools for Editing Videos<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/video\/' rel='post_tag'>video<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/video-editor\/' rel='post_tag'>video editor<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":2,"sec":23},"status":"publish","excerpt":""},{"id":25741,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/content-writing\/","name":"content-writing","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/12\/content-writing.jpg","alt":"Content writing"},"title":"Content Writing, Types, Importance, Tools ? A Complete Guide.","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Dec 13, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-12-13 03:18:51","modifiedDate":"2024-12-13 03:18:54","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-12-13 03:18:54","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/content-writing\/' rel='post_tag'>Content Writing<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/content-writing-tools\/' rel='post_tag'>Content Writing tools<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/keyword-research\/' rel='post_tag'>Keyword Research<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/keyword-research-tool\/' rel='post_tag'>Keyword Research tool<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/seo-strategies\/' rel='post_tag'>SEO strategies<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/types-of-content-writing\/' rel='post_tag'>types of Content Writing<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":5,"sec":43},"status":"publish","excerpt":""},{"id":25677,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/animation\/","name":"animation","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/12\/Animation-tips-for-beginners.jpg","alt":"Animation tips for beginners"},"title":"Animation: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Mastering the Art","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Dec 10, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-12-10 04:57:25","modifiedDate":"2024-12-10 04:57:29","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-12-10 04:57:29","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/animation\/' rel='post_tag'>Animation<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/animation-tips-for-beginners\/' rel='post_tag'>Animation tips for beginners<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/best-animation-tools\/' rel='post_tag'>Best animation tools<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/learn-animation-online\/' rel='post_tag'>Learn animation online<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":5,"sec":4},"status":"publish","excerpt":""},{"id":24996,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/quantum-computing\/","name":"quantum-computing","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/10\/Quantum-Computing-pc.jpg","alt":"Quantum Computing"},"title":"Quantum Computing: Unlocking a New Frontier in Technology","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Oct 19, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-10-19 02:31:02","modifiedDate":"2024-10-19 02:31:06","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-10-19 02:31:06","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/cryptography\/' rel='post_tag'>Cryptography<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/new-technology\/' rel='post_tag'>New Technology<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/quantum-computing\/' rel='post_tag'>Quantum Computing<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/what-is-quantum-computing\/' rel='post_tag'>what is Quantum Computing<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":2,"sec":40},"status":"publish","excerpt":""},{"id":24884,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/data-recovery\/","name":"data-recovery","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/10\/data-recovery-tips.jpg","alt":"data recovery"},"title":"How to (Data Recovery) Recover Deleted Files ?","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Oct 11, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-10-11 05:31:27","modifiedDate":"2024-10-11 05:31:31","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-10-11 05:31:31","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/best-data-recovery-software\/' rel='post_tag'>Best data recovery software<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/data-recovery\/' rel='post_tag'>Data Recovery<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/free-file-recovery-tools\/' rel='post_tag'>Free file recovery tools<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/how-to-recover-deleted-files\/' rel='post_tag'>How to recover deleted files<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/recover-deleted-files\/' rel='post_tag'>Recover Deleted Files<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":2,"sec":32},"status":"publish","excerpt":""},{"id":24901,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/speed-up-a-slow-computer\/","name":"speed-up-a-slow-computer","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/10\/Speed-up-a-Slow-Computer.jpg","alt":"Speed up a Slow Computer"},"title":"How to Speed up a Slow Computer ?","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Oct 11, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-10-11 05:31:24","modifiedDate":"2024-10-11 05:31:29","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-10-11 05:31:29","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/best-tools-to-speed-up-pc\/' rel='post_tag'>Best tools to speed up PC<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/how-to-speed-up-a-slow-computer-2024\/' rel='post_tag'>How to speed up a slow computer 2024<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/increase-computer-speed\/' rel='post_tag'>Increase computer speed<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/optimize-pc-performance\/' rel='post_tag'>Optimize PC performance<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":2,"sec":16},"status":"publish","excerpt":""},{"id":23278,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/ar-vr-mr-technology\/","name":"ar-vr-mr-technology","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/09\/ar-vr-xr-mr.jpg","alt":"AR VR MR XR"},"title":"Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR), (XR) (2024) How it works ?","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Sep 28, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-09-28 01:41:28","modifiedDate":"2024-09-28 01:41:32","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-09-28 01:41:32","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/2024-trends-and-advancements-in-ar\/' rel='post_tag'>2024 Trends and Advancements in AR<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/ar\/' rel='post_tag'>AR<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/ar-works\/' rel='post_tag'>AR WORKS<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/augmented-reality\/' rel='post_tag'>Augmented Reality<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/digital-world\/' rel='post_tag'>DIGITAL WORLD<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/extended-reality\/' rel='post_tag'>Extended Reality<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/mixed-reality\/' rel='post_tag'>Mixed Reality<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/mr\/' rel='post_tag'>MR<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/virtual-reality\/' rel='post_tag'>Virtual Reality<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/vr\/' rel='post_tag'>VR<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/xr\/' rel='post_tag'>XR<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/xr-works\/' rel='post_tag'>XR WORKS<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":6,"sec":4},"status":"publish","excerpt":""},{"id":23053,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/parts-of-a-laptop\/","name":"parts-of-a-laptop","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/09\/parts-of-laptop.jpg","alt":"Parts of a Laptop"},"title":"27 Parts of a Laptop Internal and External, With Explained","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Sep 3, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-09-03 02:26:14","modifiedDate":"2024-09-03 02:26:18","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-09-03 02:26:18","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/external-laptop-parts\/' rel='post_tag'>external laptop parts<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/important-parts-of-a-laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>important parts of a laptop<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/internal-laptops-parts\/' rel='post_tag'>internal laptops parts<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>laptop<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/laptop-internal-and-external-parts\/' rel='post_tag'>Laptop Internal and External parts<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/laptop-parts\/' rel='post_tag'>Laptop parts<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/parts-of-a-laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>Parts of a Laptop<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/what-are-the-parts-of-a-laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>what are the parts of a laptop<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":7,"sec":22},"status":"publish","excerpt":""},{"id":22183,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/computer-store-data-0-or-1\/","name":"computer-store-data-0-or-1","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/08\/Computer-Store-Data-0-or-1.jpg","alt":"Binary system"},"title":"Why Computer Store Data 0 or 1, Full Detail ?","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Aug 21, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-08-21 00:48:59","modifiedDate":"2024-08-21 00:49:02","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-08-21 00:49:02","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/computer-data\/' rel='post_tag'>computer data<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/computer-data-store\/' rel='post_tag'>computer data store<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/data-store-0-or-1\/' rel='post_tag'>data store 0 or 1<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/data-stored-0-or-1-full-detail\/' rel='post_tag'>data stored 0 or 1 full detail<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/why-computer-store-0-or-1\/' rel='post_tag'>Why computer store 0 or 1<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/why-computer-store-data-0-or-1\/' rel='post_tag'>Why Computer Store Data 0 or 1<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":4,"sec":12},"status":"publish","excerpt":"The binary system, which is the basis of all contemporary digital computing, is the reason why computers store data as 0s and 1s. This is because computers depend on the binary number system."},{"id":22160,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/cpu-gpu-tpu-and-npu\/","name":"cpu-gpu-tpu-and-npu","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/08\/cpu-gpu-tpu-and-npu.jpg","alt":"cpu gpu tpu and npu"},"title":"What is Cpu, Gpu, TPU and Npu ? How It Works ?","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Aug 20, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-08-20 00:46:18","modifiedDate":"2024-08-20 00:46:21","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-08-20 00:46:21","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/central-processing-unit\/' rel='post_tag'>Central Processing Unit<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/cpu\/' rel='post_tag'>cpu<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/gpu\/' rel='post_tag'>gpu<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/graphics-processing-unit\/' rel='post_tag'>Graphics Processing Unit<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/how-it-works-cpu\/' rel='post_tag'>How It Works cpu<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/how-it-works-tpu\/' rel='post_tag'>How It Works tpu<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/neural-processing-unit\/' rel='post_tag'>Neural Processing Unit<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/tensor-processing-unit\/' rel='post_tag'>Tensor Processing Unit<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/tpu\/' rel='post_tag'>tpu<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":4,"sec":0},"status":"publish","excerpt":"The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is sometimes referred to as the \"brain\" of the device. The majority of the work that takes place inside a computer is carried out by it. It is responsible for handling fundamental instructions and managing activities like as arithmetic, logic, control, and input\/output operations. In addition to being responsible for the operation of the operating system, applications, and other things, it handles activities that are universal in nature."},{"id":21988,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/ping\/","name":"ping","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/08\/what-is-ping.jpg","alt":"Ping"},"title":"What is Ping, Example, How it works ?","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Aug 18, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-08-18 02:22:18","modifiedDate":"2024-08-18 02:22:23","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-08-18 02:22:23","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/example-of-ping\/' rel='post_tag'>example of ping<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/how-ping-works\/' rel='post_tag'>How Ping Works<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/ping\/' rel='post_tag'>Ping<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/ping-command\/' rel='post_tag'>ping command<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/typical-ping-command-output\/' rel='post_tag'>Typical Ping Command Output<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/uses-of-ping\/' rel='post_tag'>Uses of Ping<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/what-is-ping\/' rel='post_tag'>What is Ping<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/what-is-ping-command-used-for\/' rel='post_tag'>what is ping command used for<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":3,"sec":56},"status":"publish","excerpt":"When a host (often a computer or server) is connected to an Internet Protocol (IP) network, the \"Ping\" utility tool is used to determine whether or not the host can be reached. Sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to the host that is the target of the operation and then waiting for an Echo Reply gives it the ability to function. The term \"ping\" originates from sonar technology, where it refers to the pulse of sound that is sent out via the system in order to identify things."},{"id":21472,"link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/get-a-new-laptop\/","name":"get-a-new-laptop","thumbnail":{"url":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/08\/new-laptop.jpg","alt":""},"title":"What things should check when get a new laptop?","author":{"name":"Narinder Kumar","link":"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/author\/blogsbuz-com\/"},"date":"Aug 12, 2024","dateGMT":"2024-08-12 02:45:20","modifiedDate":"2024-08-12 02:45:22","modifiedDateGMT":"2024-08-12 02:45:22","commentCount":"0","commentStatus":"open","categories":{"coma":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>","space":"<a href=\"https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/category\/basic-intermediate-advanced-computer-knowledge\/\" rel=\"category tag\">basic intermediate advanced Computer knowledge<\/a>"},"taxonomies":{"post_tag":"<a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/buy-new-laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>buy new laptop<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/check-things-when-get-a-new-laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>check things when get a new laptop<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/get-a-new-laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>get a new laptop<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>laptop<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/new-laptop-buy-tips\/' rel='post_tag'>new laptop buy tips<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/what-things-should-check-when-get-a-new-laptop\/' rel='post_tag'>What things should check when get a new laptop<\/a><a href='https:\/\/blogsbuz.com\/tag\/which-laptop-should-i-get\/' rel='post_tag'>Which laptop should I get<\/a>","table_tags":""},"readTime":{"min":3,"sec":43},"status":"publish","excerpt":"Are you looking for recommendations on new laptop, Take into consideration the following aspects when purchasing a new laptop to guarantee that it satisfies your requirements:"}]