What is Low-Level Programming?
Low-level programming involves working closer to the hardware level and understanding how computer systems operate at a fundamental level. Here’s an in-depth look at topics covered in low-level programming:
1. Computer Architecture:-
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Understanding CPU design, registers, ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), and the control unit.
- Memory Hierarchy: Types of memory (RAM, cache, ROM), memory access, and addressing.
- Machine Cycle: Fetch, decode, execute, and store stages in instruction processing.
- Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): Types of instructions, registers, and operations unique to different processors.
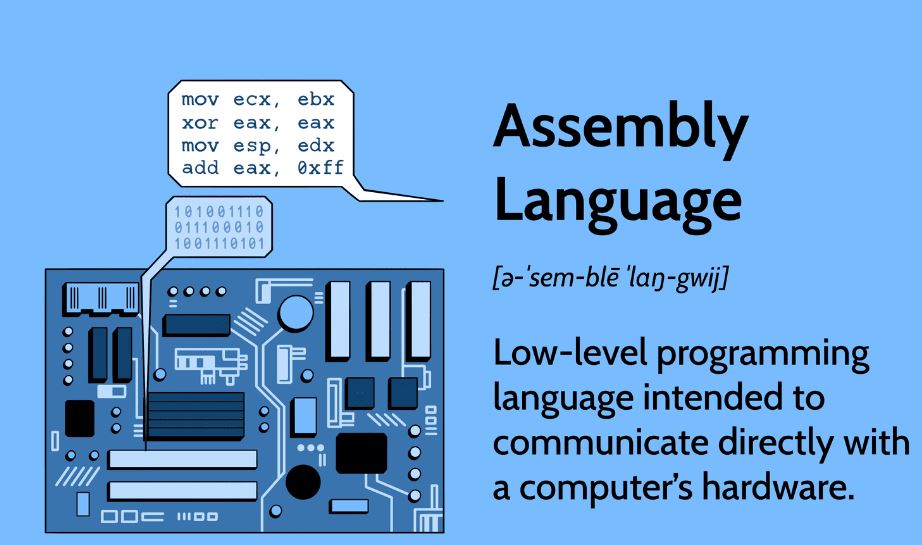
2. Assembly Language Programming:-
- Syntax and Structure: Assembly language syntax varies by CPU architecture, such as x86, x86-64, or ARM.
- Instructions: Working with common assembly instructions for data movement (MOV), arithmetic (ADD, SUB), logical (AND, OR), and control flow (JMP, CALL).
- Registers: Using registers like EAX, EBX in x86 or R0, R1 in ARM, which serve as the fastest storage locations on a CPU.
- Memory Addressing: Direct, indirect, indexed, and base-offset addressing modes for efficient data access.
- Stack Management: Push and pop operations, stack frames, and managing function calls using the stack.
3. System Programming:-
- Operating System Interfaces: Working with system calls for interacting with OS services (e.g., process management, I/O).
- Process and Thread Management: Creating and managing processes and threads, understanding context switching.
- Memory Management: Memory allocation, segmentation, paging, and virtual memory concepts.
- File System Interfaces: Understanding file descriptors, file I/O operations (open, read, write, close).

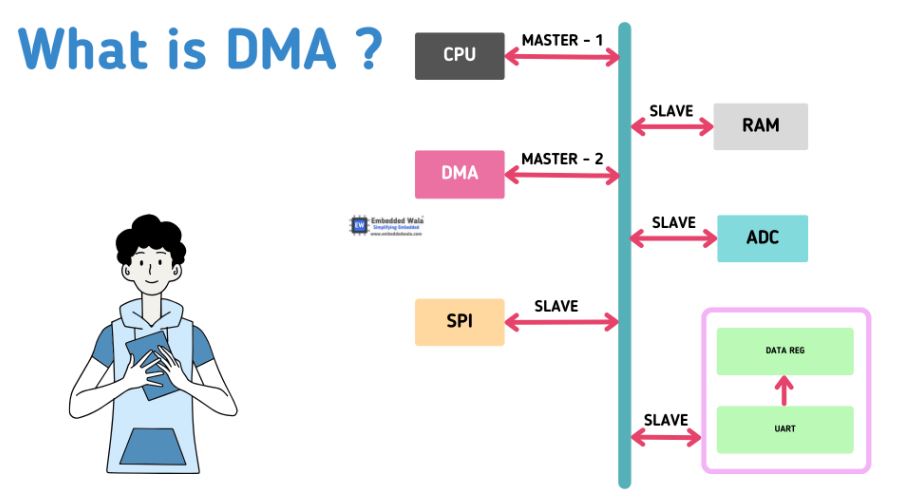
4. Pointers and Direct Memory Access:-
- Pointers in C/C++: Manipulating memory addresses directly, pointer arithmetic, and function pointers.
- Direct Memory Access (DMA): Using DMA controllers to bypass the CPU for fast data transfer between memory and devices.
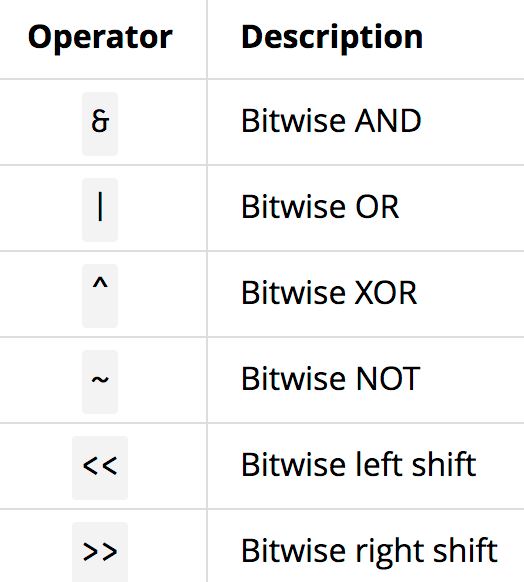
5. Bitwise Operations:-
- Binary Representation: Working with binary, hexadecimal, and octal number systems.
- Bit Manipulation: Using bitwise operators (AND, OR, XOR, NOT, shifts) to perform operations directly on individual bits.
- Flag Management: Setting, clearing, and toggling bits to manage flags in low-level programming.
6. Embedded Systems Programming:-
- Microcontrollers and Microprocessors: Programming on small, resource-constrained devices (e.g., Arduino, ARM Cortex).
- Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS): Using RTOS for scheduling and real-time constraints.
- I/O Ports and Peripheral Interfaces: Controlling and interfacing with hardware components like sensors, actuators, and communication protocols (SPI, I2C, UART).
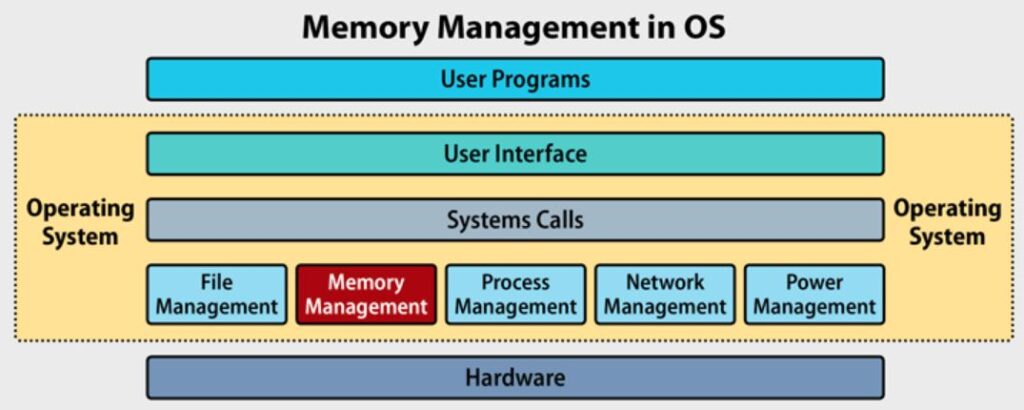
7. Memory Management and Allocation:-
- Dynamic Memory Allocation: Allocating and deallocating memory in languages like C (malloc, free).
- Memory Layout: Understanding memory layout (stack, heap, global, and code segments).
- Memory Leaks and Buffer Overflows: Identifying and handling memory leaks, buffer overflows, and implementing bounds checking.
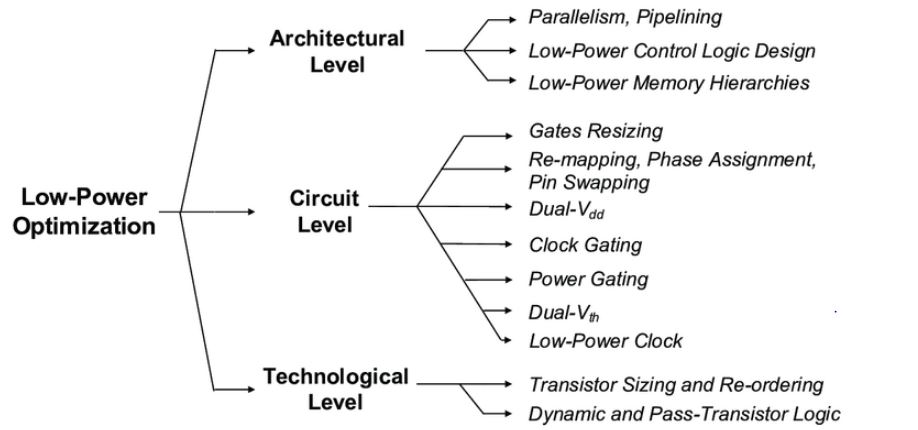
8. Low-Level Optimization Techniques:-
- CPU Cache Optimization: Writing code that takes advantage of CPU cache hierarchy (L1, L2, L3) for better performance.
- Loop Unrolling and Branch Prediction: Reducing branch mispredictions and optimizing loops to reduce CPU cycles.
- Manual Memory Management: Efficient memory usage and managing memory fragmentation.
9. Programming for Hardware Interfaces:-
- I/O Ports and Memory-Mapped I/O: Accessing hardware registers and ports directly to control peripherals.
- Bus Systems: Working with bus interfaces like PCIe, USB, and I2C for data transfer and device communication.
- Embedded Protocols: Working with low-level communication protocols like SPI, I2C, CAN, and USB for data exchange.
See More:- What is Domain Name? Types of Domain Name
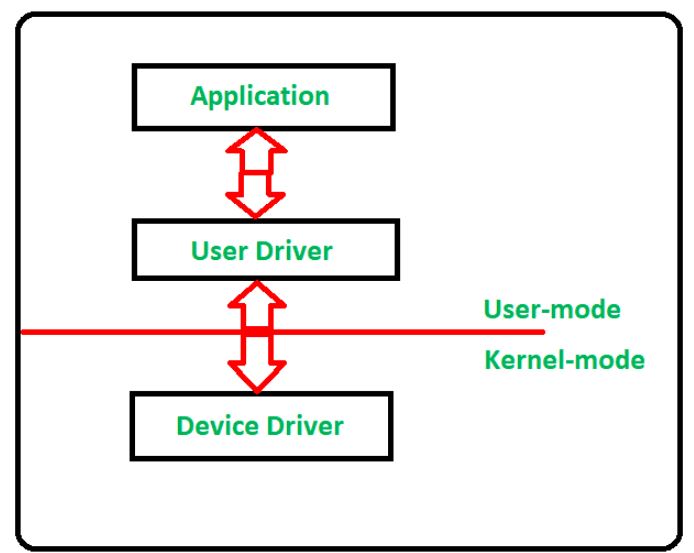
10. Kernel and Driver Development (Advanced):-
- Kernel Modules: Writing Linux kernel modules for device drivers.
- Device Drivers: Developing drivers for hardware components to enable OS-level communication.
- System Calls and Kernel Debugging: Extending OS capabilities with custom system calls and debugging at the kernel level.

Hi, I’m Narinder Kumar, founder of BlogsBuz.com. I create articles and generate celebrity biographies, providing verified, up-to-date content. As an SEO expert and online tools creator, I also share practical tips on making money online, finance management, blogging, and passive income. My mission is to provide accurate information and keep you away from fake content, ensuring you stay well-informed and make smart decisions online.


Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for stopping by BlogsBuz.com — we’re thrilled to have you! 🙌
Stay tuned for daily updates on your favorite celebrities, the latest in entertainment news, and exclusive stories you won’t find anywhere else. 🔥
If you found this post helpful, we’d love it if you shared it with your friends and followers. Let’s grow a vibrant community together and make BlogsBuz.com your go-to source for everything entertainment. 💫
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
🌟 Discover BlogsBuz.com! 🎉
Your ultimate hub for the latest celebrity news, trending entertainment stories, and exclusive behind-the-scenes scoops — all in one place! 🔥
👉 Stay updated! Subscribe now and enable notifications to never miss a new post, viral trend, or breaking entertainment update.
💌 Enjoying our content? Show some love! Share BlogsBuz.com with your friends and help us grow into the #1 destination for entertainment fans around the world. 🚀