The main parts of a laptop are broken down below, along with an explanation of each part’s purpose and how it affects the device’s overall performance:
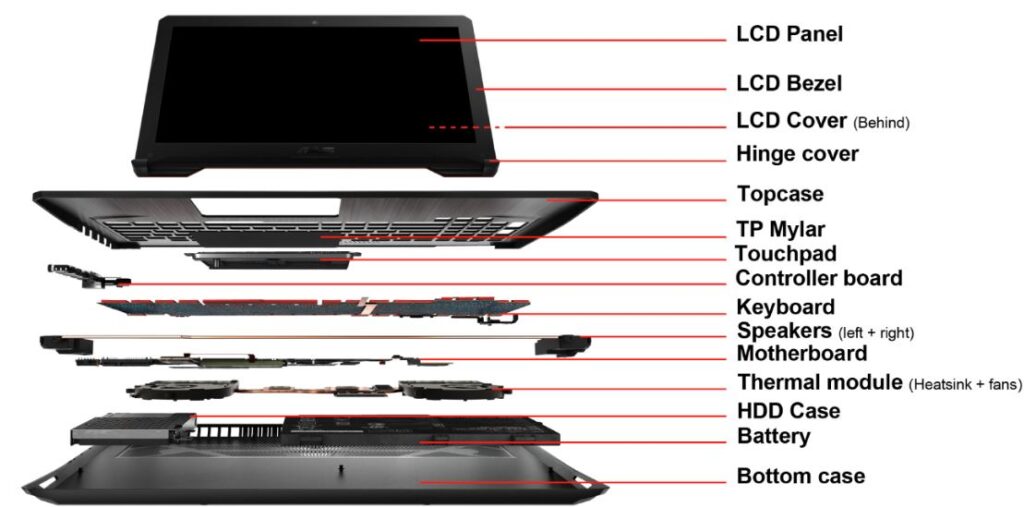
Internal Parts of a Laptop
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The central processing unit (CPU) of a internal part of laptop is its brain; it is in charge of handling tasks and carrying out commands. Everything is managed by it, including managing system resources and executing programs.
Depending on the CPU type, laptop CPUs are designed to be as energy-efficient as possible to extend battery life while still offering sufficient processing capacity for standard activities like web surfing, document editing, and, in some cases, gaming or video editing. Intel and AMD are two common laptop CPU manufacturers, with well-known variants being Intel Core and AMD Ryzen.
| Role – | The principal processor of a laptop, the CPU handles all computations and processes. It executes programs and processes data. |
| New Features – | In order to improve multitasking, CPUs in 2024 will feature several cores—up to 16 or more in top models—and allow hyper-threading. AI processing units are also included for machine learning and increased productivity. |
2. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
A laptop’s GPU, or graphics processing unit Parts of a Laptop, is a dedicated CPU used to manage graphics rendering jobs like showing pictures, movies, and interactive games. By removing these activities off the CPU, it improves speed and produces smoother images in graphics-intensive applications such as video editing, 3D modeling, and gaming.
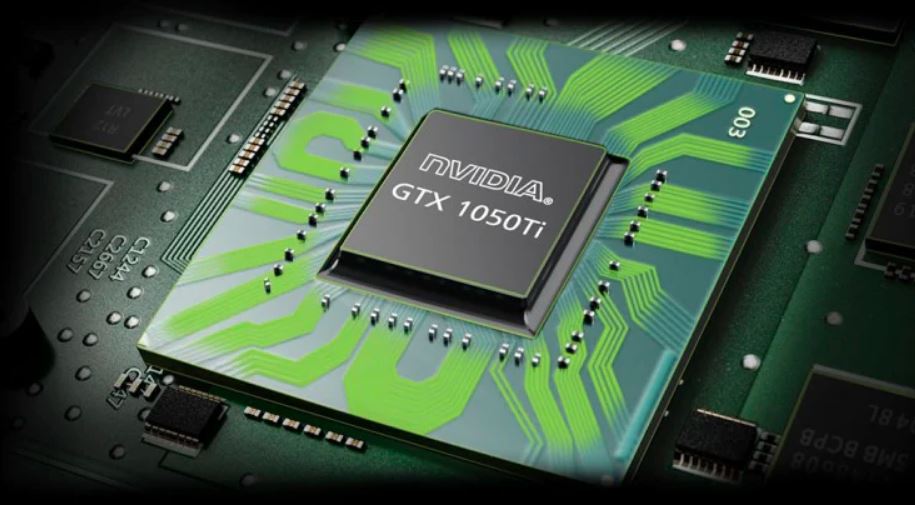

Dedicated GPUs, which are independent parts with their own memory for improved performance, or integrated GPUs, which are incorporated into the CPU and share system memory, are two types of GPUs available for laptops. Popular laptop GPU manufacturers include AMD and NVIDIA.
| Role – | Rendering of pictures, movies, and animations is done by the GPU. It’s essential for 3D modeling, video editing, and gaming. |
| New Features – | Powerful discrete GPUs with AI-enhanced visuals, real-time ray tracing, and large VRAM capacities are standard on modern laptops for demanding graphical workloads. |
3. Memory (RAM)
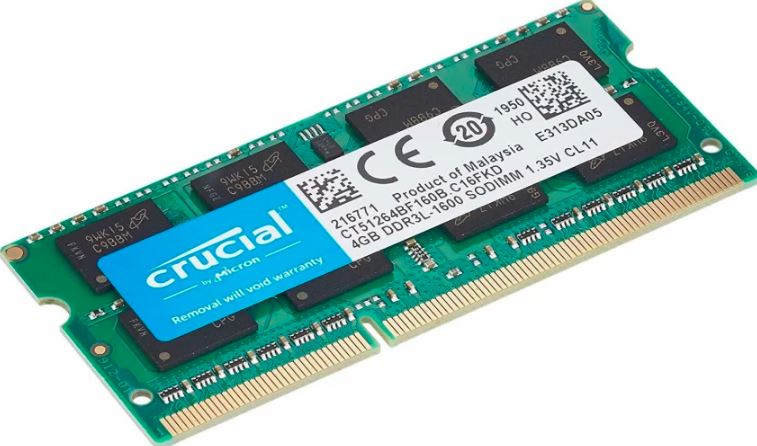

Random Access Memory, or RAM, on a laptop is its short-term memory that is used to store and retrieve data that the CPU need to execute applications. A laptop with more RAM can run more apps at once and has better overall system responsiveness. A software or file is loaded into RAM when you open it from the laptop’s storage so the CPU can access it fast. A laptop’s capacity to multitask and run memory-intensive programs, such as complex games or video editing software, may be impacted by the RAM capacity of the device.
4. Storage (SSD/HDD)
SSD (Solid State Drive): utilized mostly for files that need quick access, programs, and the operating system. This optimizes system speed, shortens boot times, and boosts overall performance, which makes it perfect for activities like video editing, gaming, and fast file access.
HDD (Hard Disk Drive): usually used to store massive volumes of data, including backup copies, audio, video, and picture files. It is less expensive than an SSD, although it is not as fast for large-scale storage.
| Role – | The operating system, programs, and data on a laptop are kept on storage devices. Solid State Drives, or SSDs, outperform Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) in terms of speed and dependability. |
| New Features – | NVMe SSDs are widely used because they provide quick read/write speeds, short boot times, and better application performance. Storage capacity span several terabytes to as much as 256GB. |
5. Cooling System
The parts of a laptop’s cooling system is to control the heat produced by the GPU, CPU, and other internal parts.
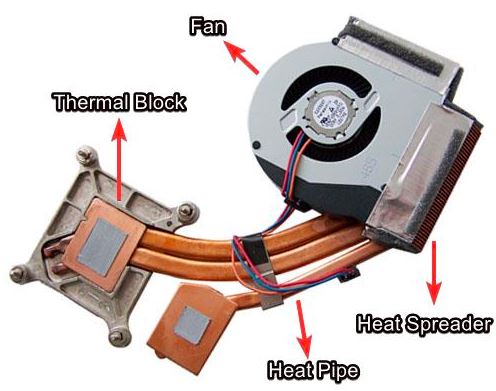
6. Motherboard
The primary circuit board that connects and facilitates communication between the parts of a laptop’s CPU, GPU, RAM, storage (SSD/HDD), and other peripherals is called the motherboard. It contains crucial chipsets for controlling connection, power distribution, and data flow.
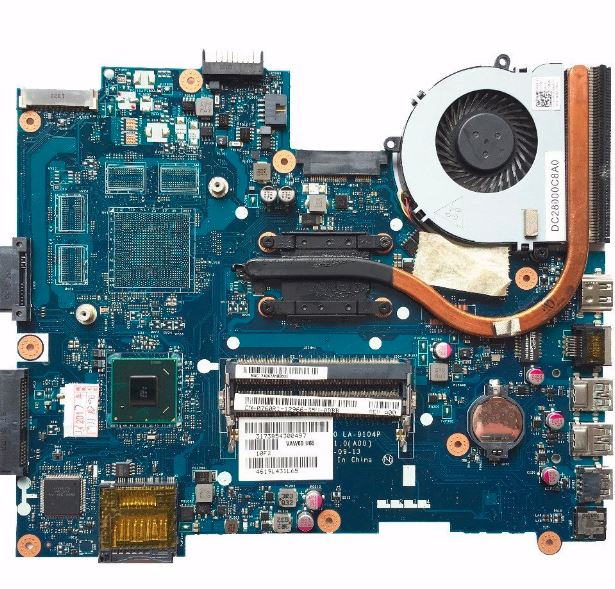
Among the motherboard’s primary functions are parts of a Laptop:
- Connecting Components: It offers the channels by which information moves from the CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage.
- Distributes electricity to the components from the battery or charger via power management.
- Peripheral Support: Contains ports for attaching displays, audio, and USB devices from outside the system.
7. Battery
The rechargeable power source that powers a laptop while it’s not hooked into an electrical outlet is called a laptop battery. It supplies the energy required to operate the laptop’s internal parts, including the CPU, GPU, and display, in the absence of an external power source.

| Role – | When the laptop is not linked to an external power source, it is powered by its battery. |
| Features – | Solid-state batteries have a longer lifespan and charge more quickly. A single laptop charge may last anywhere from 8 to 20 hours, depending on use. |
8. Power Supply Unit (PSU)
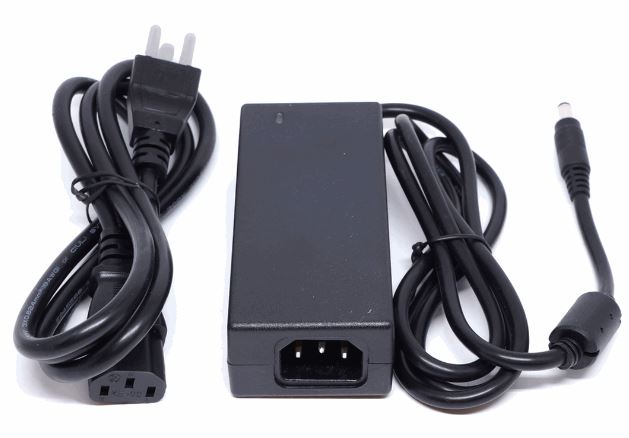

The power supply unit, or PSU, parts of a laptop is usually built within the charger, often referred to as the power adapter or AC adapter. It converts the alternating current (AC) electricity coming from a wall outlet into direct current (DC), a lower voltage that the laptop may safely consume.
9. BIOS/UEFI Chip
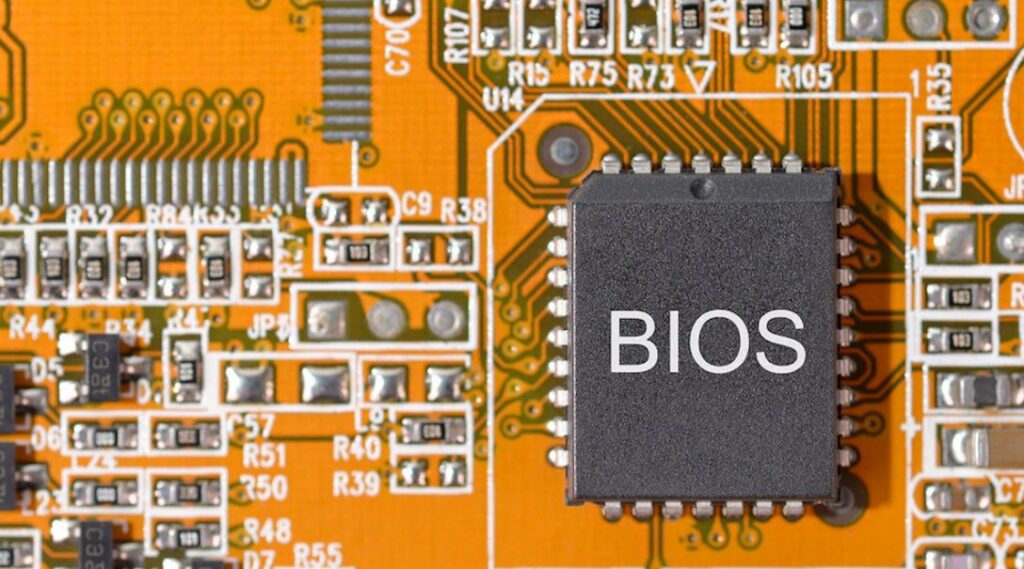
Role: This chip serves as a configuration interface and holds the firmware that initializes devices upon booting.
Features: Because UEFI offers a more user-friendly interface and speedier boot times, BIOS has generally been supplanted.
10. Internal Speakers
Role – These small speakers output sound from the parts of laptop.
Features – Laptops are equipped with quadruple or stereo speaker systems that use advanced audio technologies like Dolby Atmos to provide a more immersive sound.

11. Wi-Fi Card
| Role – | Internet access via wireless is made possible by the Wi-Fi card. |
| Features – | Wi-Fi 7 cards handle numerous devices with reduced latency and provide quicker speeds and higher stability. |

12. Touchpad Controller
A laptop’s touchpad controller is a (parts of a Laptop) dedicated chip or circuit that controls the touchpad’s input, enabling it to recognize and comprehend finger motions. These motions are translated into clicks, gestures, and pointer movements on the screen.

Role – Gestures and cursor movement are made possible via the touchpad controller, which interprets inputs from the touchpad.
Features: Larger, more sensitive touchpads with haptic feedback provide a more tactile user experience.
13. Bluetooth Module
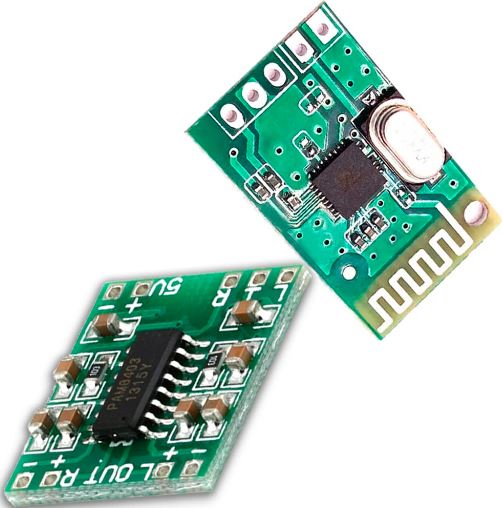
Role – With the help of this module, the laptop may wirelessly connect to keyboards, mouse, and headphones.
Features – With its increased range, speed, and energy economy, Bluetooth 5.3 is standard.
14. Sensors
| Role – | Numerous sensors, including fingerprint readers, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and ambient light sensors, are found in laptops. |
| Features – | By allowing functions like adjustable brightness, secure biometric logins, and automated screen rotation, these sensors improve user experience. |
15. Optical Drive (Rare)
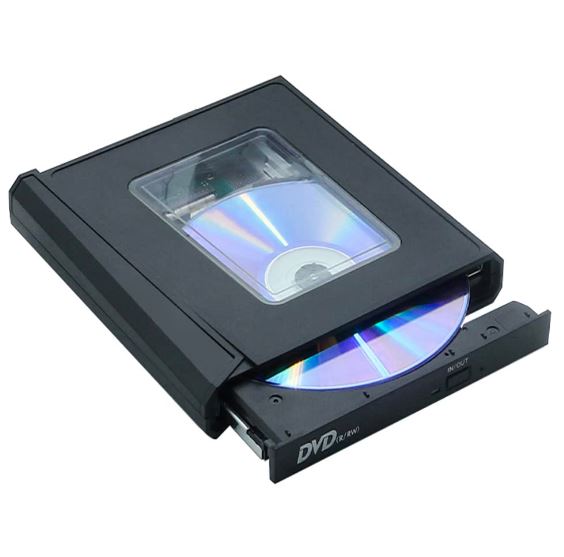

Role – Data on CDs, DVDs, and Blu-rays may be read and written by an optical drive.
Features – In contemporary laptops, optical drives are uncommon since most manufacturers concentrate on creating thinner models. If necessary, external USB optical drives are offered.
External Parts of a Laptop
1. Display (Screen)
Features – High-resolution screens parts of a Laptop, such 4K OLED or mini-LED panels, with high refresh rates (120Hz to 240Hz), compatibility for HDR, and touch functionality are features found on some laptop models.

2. Keyboard
Features – Keyboards often include parts of a Laptop, mechanical or membrane switches, RGB illumination that may be customized, and backlighting. Per-key illumination and programmable macros are available on some models.

3. Touchpad
Features – Larger, multi-touch capable, and often equipped with haptic feedback for increased responsiveness are features of contemporary touchpads.

4. Microphone
Features – More sophisticated microphones use noise-canceling technology to cut down on background noise and improve speech quality.

5. Webcam
Features – 1080p or 4K cameras with AI features like automated framing, background blur, and facial recognition for safe logins are standard on laptops.

6. Speakers
Features – Immersion sound quality is achieved using high-fidelity stereo or quad speakers that use sophisticated audio processing.

7. Ports
Features – SD card readers, HDMI 2.1, Thunderbolt 4, USB-C, and headphone jacks are examples of common ports. USB-C connectors are often used for data transmission as well as power supply.

8. Chassis (Body)
Features – Laptops are made of sturdy materials like magnesium alloy, carbon fiber, or aluminum and often have svelte, light designs. Certain types are modular, making upgrades and maintenance simpler.

9. Lid (Cover)
Features – Glass and metal are two possible materials for the lid, which may also contain a privacy shutter for the camera. Some lids have touch panels or monitors built right in.

10. Hinges
Features – Convertible laptops have stronger hinges that rotate 360 degrees, enabling tablets to be used on them.

11. Vents and Air Intakes
Features – Laptops use sophisticated cooling systems, such as liquid cooling and vapor chambers, along with more thoughtfully positioned vents.
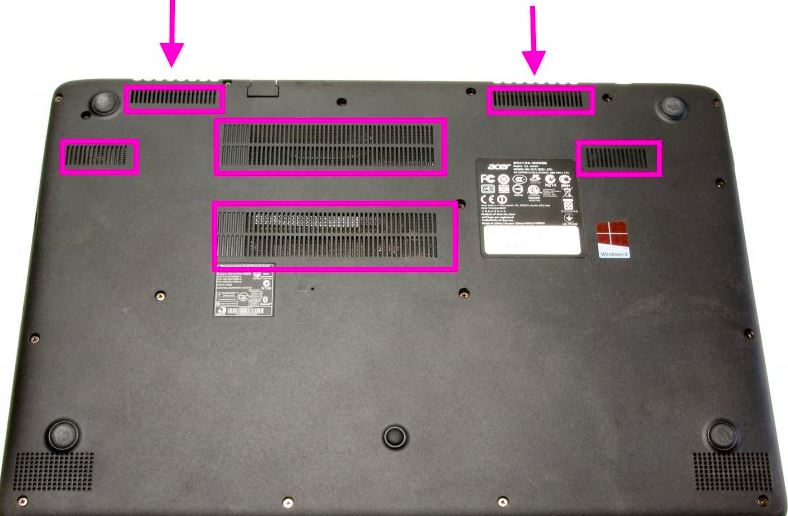
12. Rubber Feet
Features –Contemporary computers are designed to be sturdy and low-profile, with rubber feet that can be replaced or adjusted.

See more:-

I am expert skilled in SEO content Creation. My name is Narinder Kumar. I have an experience in creating websites, (SEO) Content Creation , Articles Blogs & more. Currently I prepared a SEO Content in Eduction Purpose, Entertainment, Finance Management etc.

